Are you struggling to fix a 403 forbidden error? Well, worry not. We have 7 proven ways to fix the 403 forbidden error on your website so that you can resume working without disruptions.
A 403 forbidden error can cause stress and confusion, as it locks you out of pages or resources on your website. Not being able to access your website can slow down updates, new releases, and business in general.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through some methods to fix the 403 forbidden error so that you are equipped with the knowledge to resolve the issue and focus on improving your website and users’ experience.
What Does 403 Forbidden Mean?
A 403 Forbidden Error means that you are not allowed to access the page or resource you’re trying to reach on the website. Essentially, the server understands your request but refuses to authorize it.
This could happen because the resource you are trying to access is restricted to certain users or requires specific credentials that you haven’t provided.
A 403 error could be the result of misconfigurations on the server or website. Usually, rectifying these permission and configuration errors can resolve the issue and restore your access.
If you face a 403 forbidden error, the first step must be to review your server and website settings.
What Causes a 403 Forbidden Error?
If you are wondering, “Why do I get 403 forbidden errors?” Here are the issues that may cause this error to pop up on your screen.
- Incorrect File Permissions: Every file and directory on your website has permissions that control user access. If these permissions are set incorrectly, you will be prevented from accessing specific pages.
- .htaccess File Errors: This configuration file is crucial for managing your site’s URL structures and access permissions. Errors in the .htaccess file can result in a 403 error.
- Security Plugins: WordPress security plugins aim to protect your site but sometimes block legitimate users by mistake, causing a 403 error.
- Server Configuration Issues: Misconfigurations on the web server can mistakenly restrict access to certain resources on your site.
Getting 400 bad request error on your website? Here are 6 proven ways to Fix 400 Bad Request Error in Elementor.
How to Fix 403 Forbidden Error [Proven Methods]
Now, let’s answer the real question—how to get around 403 forbidden errors? There are many methods you can use. Since the cause of the issue is not easy to diagnose, you might have to try more than one of these methods to fix the 403 forbidden error.
IMPORTANT: Before you proceed with any of the fixes listed below, make sure to back up your website. This precaution will keep your data safe and recoverable if anything goes amiss during troubleshooting.
1. Refresh the Page and Verify the Address
One of the simplest yet often overlooked to fix 403 Forbidden Error is to refresh the page and verify the web address. This error can sometimes appear due to temporary issues with the website or a miscommunication between your browser and the server.
Refreshing the page allows your browser to attempt to reconnect to the server, potentially resolving any transient errors.
Why this solution works:
- Temporary Glitches: Websites can experience momentary hiccups due to server overload, maintenance, or network issues. A refresh signals your browser to make a new request, which might succeed if the glitch has been resolved.
- URL Errors: Typographical errors in the web address can lead to a 403 Forbidden Error. Ensuring the URL is correct is the simplest step in troubleshooting.
The best time to apply this fix is after you’ve received the status code 403 forbidden error for the first time. This method also works if you manually typed the URL or followed a potentially outdated link.
To try this method, simply:
- Hit the refresh button on your browser or press F5/Ctrl+R.
- Carefully check the URL in the address bar. For example, if the intended page was https://qa.theplusaddons.com/elementor-widget/, ensure there are no typos like https://qa.theplusaddons.com/widgest or omissions like https://qa.theplusaddons.com/ without the specific path to ‘widgets.’
2. Adjust Your File Permissions
In web hosting and content management systems like WordPress, file permissions secure your website and control access to its files and directories.
Incorrect file permissions can lead to a403 forbidden request forbidden by administrative rules error, as the server restricts access to these resources for users or even the website’s scripts.
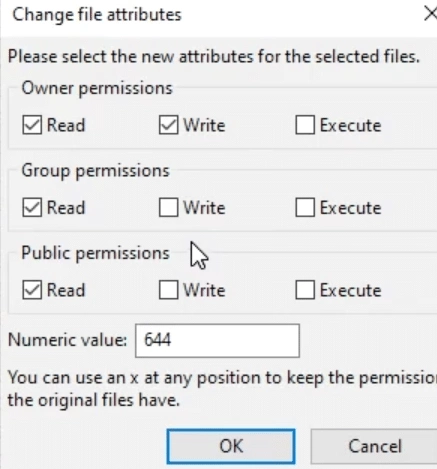
Permission Types
File permissions determine the actions that users and scripts can perform on a file or directory. These actions are categorized as:
- Read (r): Permission to view the file’s contents.
- Write (w): Permission to modify or delete the file.
- Execute (x): Permission to run the file as a program.
Permissions are represented numerically, with each action assigned a value: read (4), write (2), and execute (1). The sum of these values defines the level of access. Permissions are set for three types of users:
- Owner: The file’s creator.
- Group: Users who are part of a defined group.
- Public: Everyone else.
Indicating Permissions
Permissions are often displayed as a three-digit number, with each digit representing the owner, group, and public permissions, respectively.
For example, 755 means:
- The owner can read, write, and execute (7 = 4+2+1).
- The Group can read and execute (5 = 4+0+1).
- The public can read and execute (5 = 4+0+1).
Ideal Permissions for WordPress
For a WordPress site, the recommended permissions are:
- Directories: 755 or 750.
- Files: 644 or 640.
- wp-config.php: 600
Here is how you can change file permissions:
Step 1: Access Your Site via FTP or File Manager
Use an FTP client or the file manager provided by your hosting control panel to access your website’s files.
Step 2: Navigate to the Root Directory
Locate the root directory of your WordPress installation. It usually contains folders like wp-admin, wp-content, and wp-includes.
Recommended Read: How to Find Root Directory of WordPress Website
Step 3: Adjust Directory Permissions
Right-click on the wp-admin, wp-content, and wp-includes folders. Select ‘File Permissions‘ or a similar option.
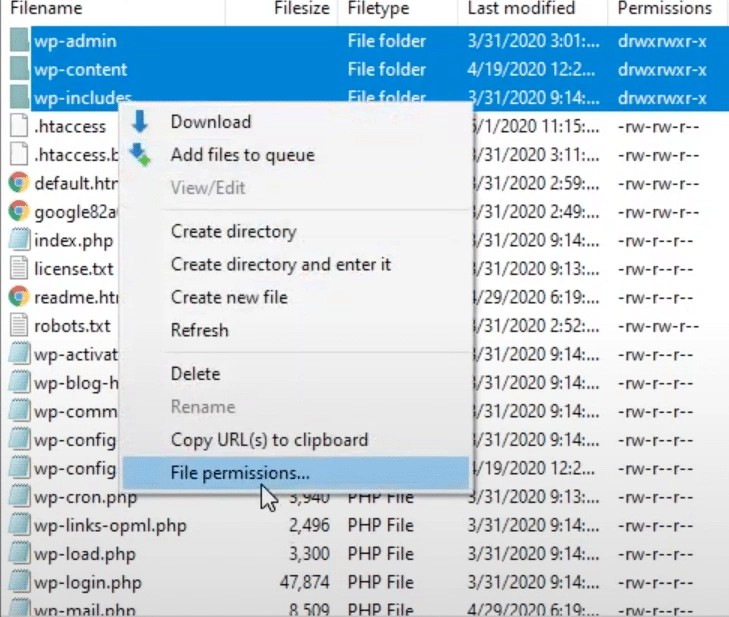
Set the numeric value to 755 or 750. Apply to directories only. Most FTP clients can apply the permission changes to subdirectories recursively.
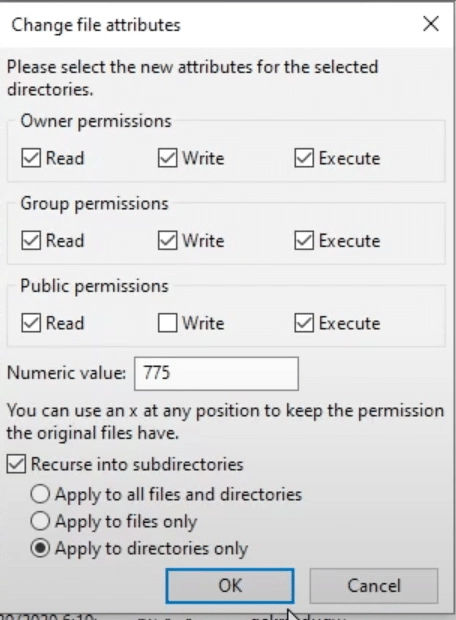
Step 4: Adjust File Permissions
Follow a similar process for files: set the permissions to 644 or 640. Ensure wp-config.php is set to 600 for increased security.
Step 5: Verify Changes
After adjusting permissions, refresh your website to see if the 403 error persists.
If your FTP client supports it, consider changing file permissions in bulk to save time. However, be cautious and ensure you’re only changing permissions for WordPress files and directories.
Adjusting file permissions is a delicate operation that can impact your website’s security and accessibility. It is important to take extra care when resetting these permissions to keep your website safe from threats.
Facing a “Web server is returning an unknown error” issue? Here’s how to fix 520 Error while trying to edit with Elementor.
3. Remove and Restore the .htaccess File
The .htaccess file in a WordPress site is a powerful configuration file used by the Apache webserver to manage website settings related to security, URL redirection, and how traffic is handled.
Incorrect settings or corrupt .htaccess files can often lead to a 403 Forbidden Error, as they may improperly restrict access to the website.
Fortunately, removing and restoring this file can rectify such issues, allowing your site to function correctly again.
To remove and restore the .htaccess File:
Step 1: Backup Your .htaccess File
Before making changes, download the current .htaccess file via FTP or file manager as a backup. This step ensures you can revert changes if needed.
Step 2: Disable the .htaccess File
Locate the .htaccess file in the root directory of your WordPress installation or file manager. This is usually where you find the wp-admin, wp-content, and wp-includes folders.
To disable the .htaccess file, simply rename it to something else. Don’t worry; this is temporary, and it is necessary to check if the file is the cause of the error.
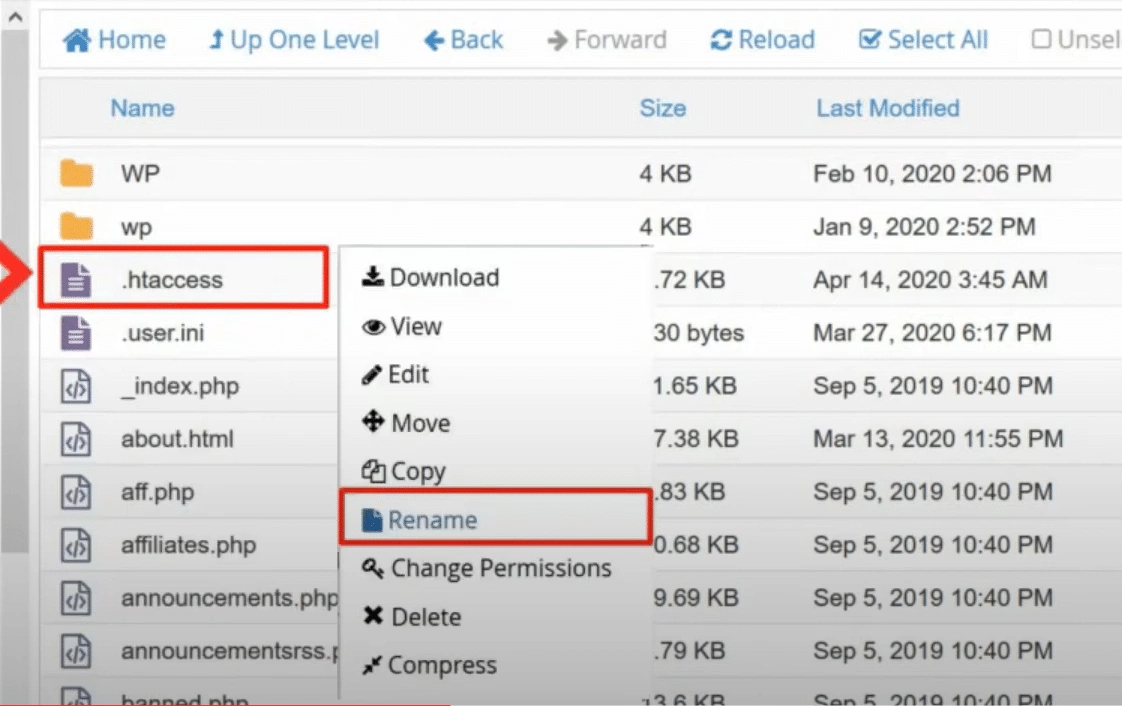
Step 3: Check Your Website
After deleting the .htaccess file, visit your website to see if the 403 Forbidden Error persists. If the error is resolved, the issue was with your .htaccess file.
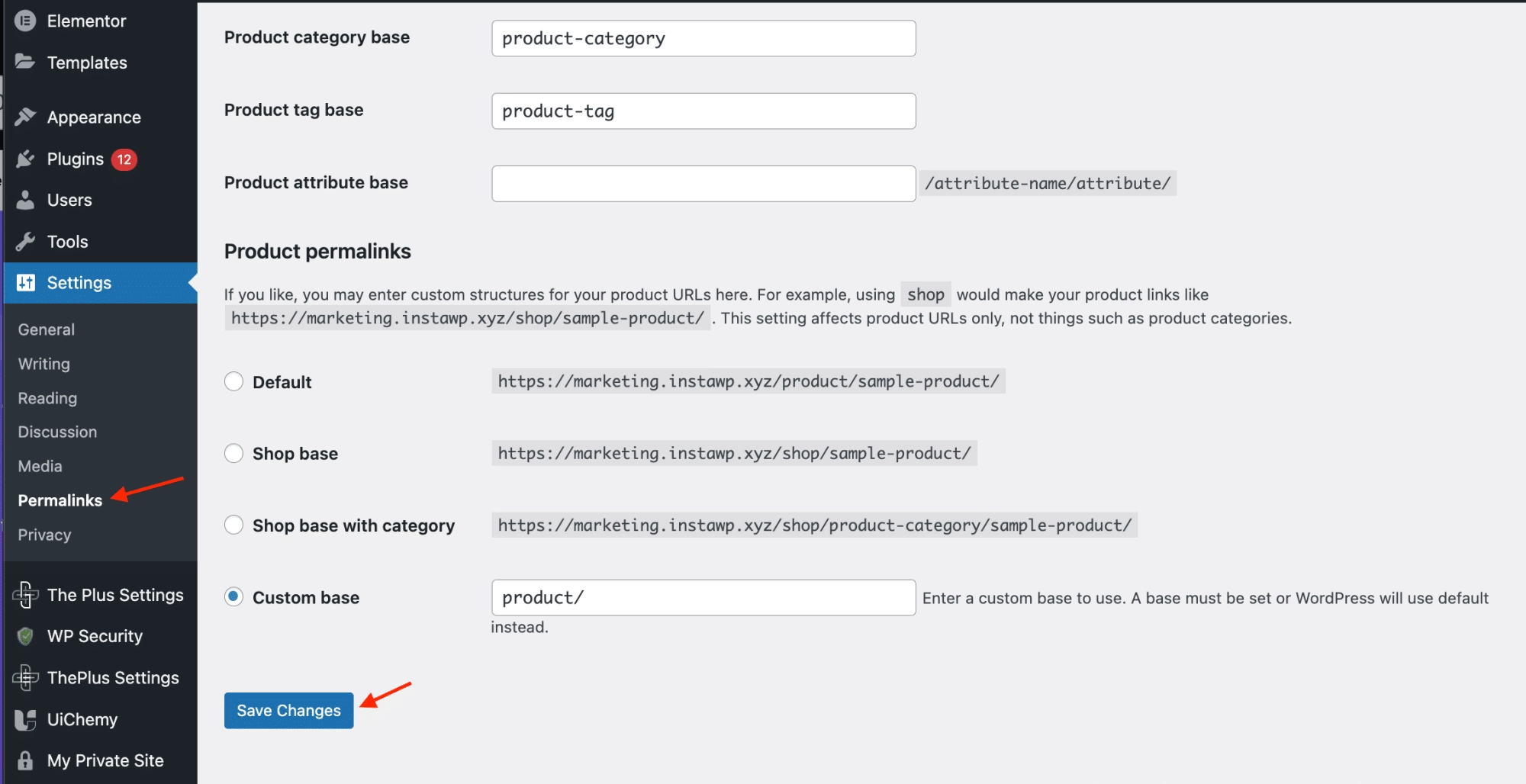
Step 4: Restore the .htaccess File
Go to your WordPress admin area, navigate to Settings > Permalinks, and simply click “Save Changes” without making any modifications.
WordPress will automatically generate a new .htaccess file with default settings.
If removing the file solves the error, consider manually editing your backup .htaccess file to remove or adjust specific directives that might be causing the issue.
Use a plain text editor and consult WordPress documentation for guidance.
4. Disable WordPress Plugins
Plugins enhance the functionality of WordPress sites, but they can sometimes conflict with each other or with the core WordPress files, leading to issues like the 403 Forbidden Error.
Disabling plugins is a recommended troubleshooting step to identify if a plugin is the cause of this error.
Why Disabling Plugins Helps
- Conflict Resolution: Disabling all plugins helps determine if the error is due to a plugin conflict.
- Isolation Technique: Once the error is resolved by disabling all plugins, you can reactivate them one by one to identify the problematic plugins.
To disable WordPress plugins:
Step 1: Access Your Site’s Backend
Use FTP or the File Manager in your hosting control panel to access your site’s files.
Step 2: Navigate to the Plugins Directory
Go to the /wp-content/ folder and find the plugins directory.
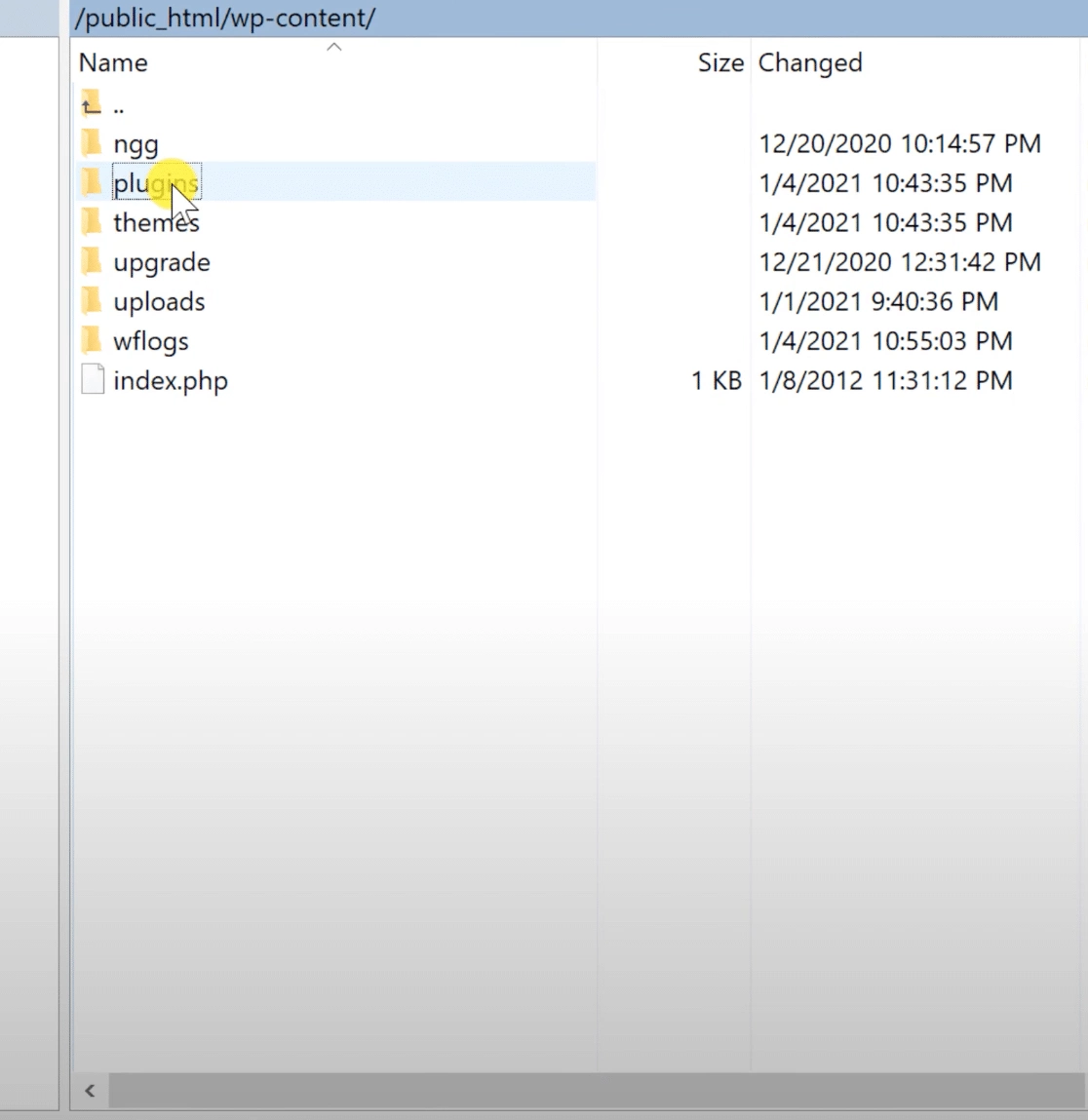
Step 3: Disable Plugins
Rename the plugins directory to something like plugins_old. This action deactivates all plugins simultaneously since WordPress can no longer find them.
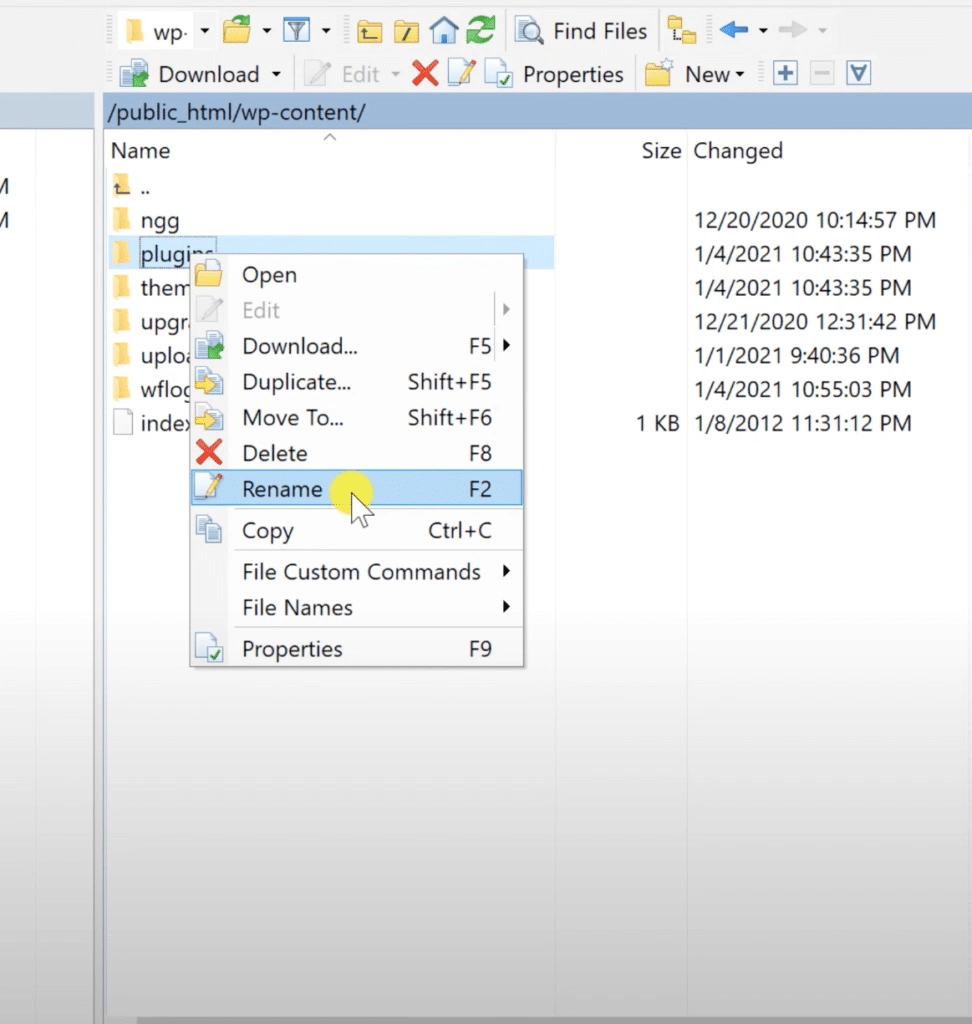
Step 4: Check Your Site
After renaming the directory, check your website to see if the 403 error persists. If the site works, a plugin was causing the issue.
Step 5: Identify the Problematic Plugin
Change the plugins_old directory back to plugins. Reactivate each plugin one by one through the WordPress dashboard, checking your site after each activation to find the culprit.
Encountering the frustrating “Update Failed” or “Publishing Failed” error messages? Here’s how you can fix WordPress update and publish failed errors!
5. Check for Malware
Malware infection is a serious concern for any website owner, as it can lead to various issues, including the 403 Forbidden Error.
Malicious software can modify your website’s files and settings, restrict access to content, or even take control of your site, prompting such errors to occur.
Identifying and removing malware is crucial for restoring your website’s functionality and security.
Why Checking for Malware is Important
- Security: Malware can compromise your website’s security and the security of your visitors.
- Website Integrity: Ensuring your website is malware-free helps maintain its integrity and trustworthiness.
To Check for and Remove Malware:
Step 1: Use a Security Plugin or Service
Install a reputable WordPress security plugin that includes malware scanning and removal features.
Step 2: Manual Inspection
Check recently modified files, as these can be indicative of a malware infection. Look for unfamiliar files or code within your website’s directories.
Step 3: Use Security Services
Consider employing a professional security service to conduct a thorough malware scan and removal process if the infection is beyond what can be handled through plugins.
Step 4: Update and Clean
Ensure all WordPress core files, plugins, and themes are up to date. Remove any unused plugins or themes that could be potential vulnerabilities.
After you identify and remove the malware, ensure that you:
- Change Passwords: Change all passwords associated with your website, including WordPress admin, FTP, and database passwords.
- Implement Security Measures: Strengthen your website’s security by implementing measures such as a web application firewall (WAF), secure passwords, and regular backups.
6. Clear Your Browser Cache and Cookies
Sometimes, the solution to a 403 Forbidden Error lies not with the website but within the browser itself.
Stale cache and cookies can cause your browser to load outdated or corrupted data, leading to access issues like the 403 error.
Why Clearing Cache and Cookies Helps
- Outdated Information: Prevents your browser from using old data to access websites.
- Corrupted Data: Removes potentially corrupted cache and cookie files that could cause access issues.
To clear your browser cache and cookies –
Step 1: Access Browser Settings
Navigate to your browser’s settings or preferences. This option is usually found in the menu in the upper-right corner of your browser.
Step 2: Find the Clear Browsing Data Option
Look for an option that says “Clear browsing data,” “History,” or “Privacy & Security.”
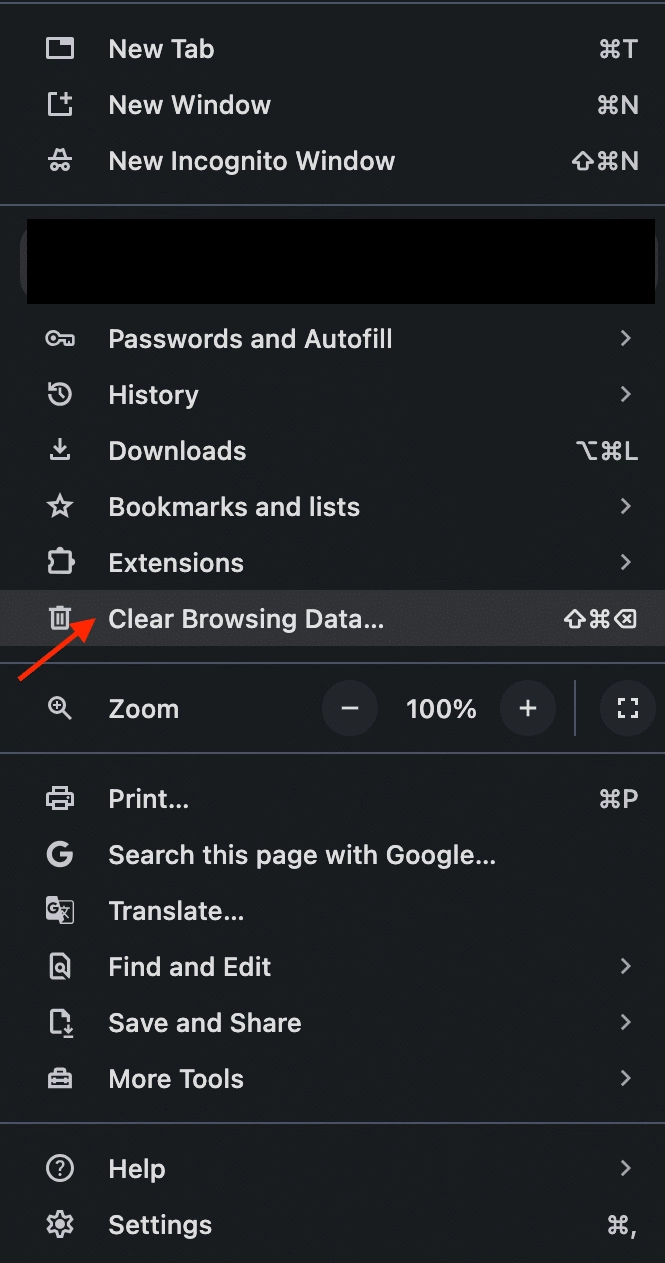
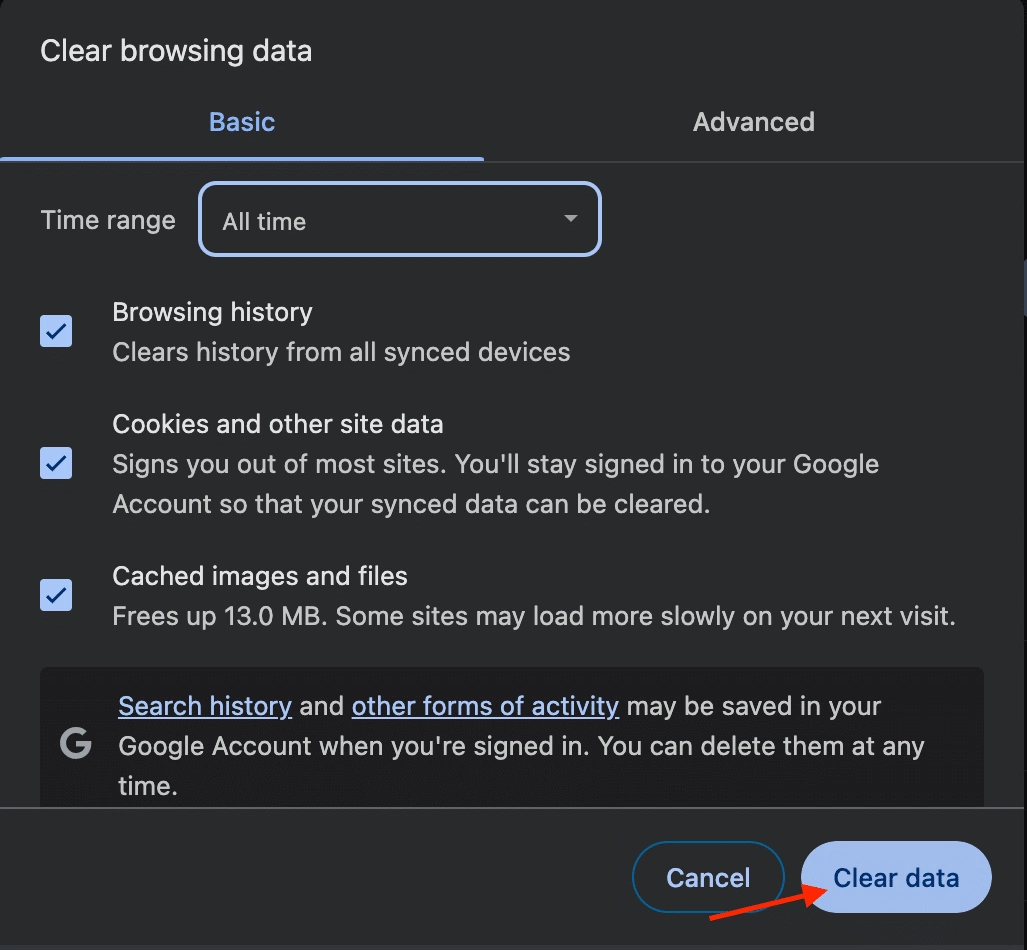
Step 3: Clear Cache as well as Cookies
Choose to clear both cache and cookies. You may also have the option to select the time range to clear (e.g., the last hour, the last day, all time).
Confirm your selection and clear the data.
7. Contact Your Hosting Provider
Lastly, if you’ve tried all the methods to fix 403 forbidden errors and still face the issue, it might be time to get in touch with your hosting provider.
Sometimes, the problem could stem from the server side, such as configuration errors, server permissions, or security settings that only your host can resolve.
Hosting providers often have insights into server logs and configurations that are not directly accessible to you, which can pinpoint the exact cause of the error.
Wrapping Up
The frustrating yet common 403 forbidden error has many fixes you can try. If you face a 403 forbidden error, refresh your page, check for inaccuracies in the domain address, and clear your browser cookies and cache.
If these methods do not work, log into your FTP client or file manager to modify permission, remove .htaccess, and disable plugins.
Before you try any of the methods mentioned in this blog, remember to store a backup of your website.
Lastly, if you’re an Elementor user, we would recommend you use The Plus Addons; this all-in-one plugin enhances your WordPress site’s functionality while prioritizing security.